AR coating, why and how?
From horticultural perspective, more sunlight coming into the greenhouse means more light onto the plants, which will lead to higher attainable yield. An article from WUR (Wageningen University & Research) claimed that “In greenhouse horticulture there is a golden rule: 1 percent more light ensures 1 percent more yield. (Research, 2019)” There are two ways to increase the light transmittance: reduce the light absorption by adjusting the material, or reduce the light reflection by add AR (Anti-Reflective) coating.
Anti-reflective coating (AR coating) is a technology of creating thin layer on surface of glass aiming at gaining a higher light transmittance level by reducing the light reflective level. But how does it work? Firstly, we must know some basic background knowledges:
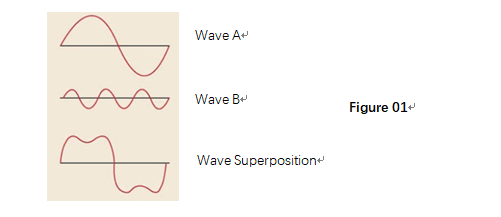
Light is a kind of wave. It has crest and trough;
Wave is a fluctuation; different waves will interact on each other (Figure 01). When the crest meets the through, the comprehensive wave becomes weaker;
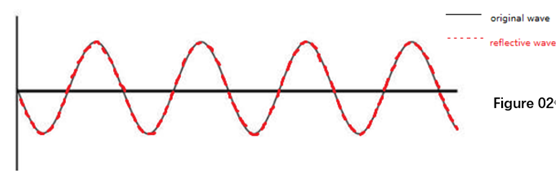
So, when the sunlight hit the glass without AR coating. It will be like that in the following image. The reflection will be a mirror image of the coming light on vertical axis. (Figure 02)
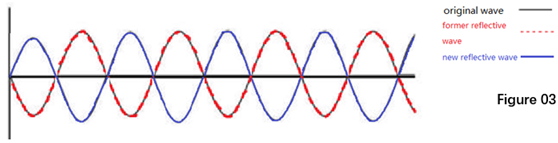
Once there is an AR coating, it will create new reflective light wave path on the coating surface. Since the thickness of the coating is 1/4 length of the light wave, the new reflective light wave will be a mirror image of the former reflective light wave on horizontal axis. (Figure 03).
According to the wave superposition theory, those two reflective lights are neutralized. From a macro perspective, the reflection is reduced. It is how the AR coating works.
Tags:anti-reflective glass diffuse glass agricultural greenhouses glass greenhouse venlo greenhouse AR glass greenhouses glass agricultural glass horticultural glass #greenhouseglass #Antireflectiveglass #Diffusetemperedglass #Ultrawhitefloatglass #agriculturalgreenhouseglass #diffuseglass #horticulturalglass #Tomatogreenhouse #Coloredpeppergreenhouse #Lettucegreenhouse #Agriculturalgreenhouse #ARglass #venlogreenhouse #greenhouseglass #Antireflectiveglass #Diffusetemperedglass #Ultrawhitefloatglass #agriculturalgreenhouseglass #diffuseglass #horticulturalglass #Tomatogreenhouse #Coloredpeppergreenhouse #Lettucegreenhouse #Agriculturalgreenhouse #ARglass #venlogreenhouse #GlassManufacturer #invernadero #ArchitecturalGlass #ClearFloatGlass #FloatGlass
Previous:Why diffuse light matters?