How to ventilate the glass greenhouse
The purpose of glass greenhouse ventilation is to remove the waste heat and moisture in the greenhouse, adjust the air composition in the greenhouse, and eliminate harmful gases, so that the ambient temperature, humidity and air conditions in the greenhouse are suitable for the requirements of plant growth.

natural ventilation
The glass greenhouse relies on natural ventilation to regulate the indoor environment most of the time. The structure of large-scale production glass greenhouses is generally a double-slope multi-span greenhouse, and the ventilation method is to set up ventilation windows on the side walls and roof ridges. The total ventilation area is not less than 15% of the greenhouse area, preferably more than 30%. When the roof ridge window is opened, the window sash should preferably be inclined upward beyond the horizontal plane. When fully opened, it forms an angle of 100 with the horizontal plane to obtain a good ventilation effect. The amount of natural ventilation is related to wind speed, wind direction, position of ventilating window, area of ventilating window, and temperature difference between inside and outside the greenhouse. When the total area of the ventilating windows is 27% of the indoor floor area, if only the ridge is ventilated, even if the outdoor wind speed reaches 10 km/h, the ideal air exchange rate of 0.75 times per minute will not be achieved; when the ridge ventilating windows and side walls When the ventilation windows are fully opened, the air exchange rate can reach 0.68 times/minute under almost no wind, which is close to the normal recommended air exchange rate of 0.75 times/minute.
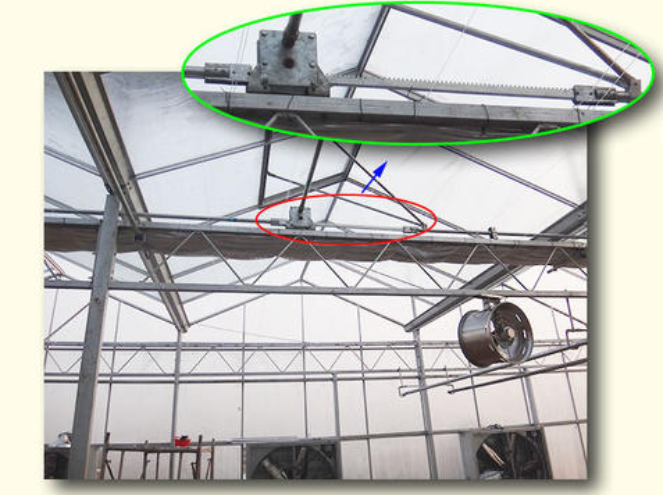

Forced ventilation
Although glass greenhouses rely on natural ventilation to adjust the environment most of the time, when summer temperatures are high, especially in hot weather when the outdoor temperature exceeds 33°C, when natural ventilation alone is difficult to meet the greenhouse cooling requirements, forced ventilation and other measures are adopted. Cooling is a common method in production. Forced ventilation is the use of fans to convert electrical or other mechanical energy into wind energy, forcing air to flow to ventilate the greenhouse and achieve a cooling effect. The theoretical cooling limit of forced ventilation is that the indoor air temperature is equal to the outdoor air temperature. Because at this time, the temperature difference between inside and outside the greenhouse is zero, and the ventilation is infinite, which is impossible in practical applications. Due to the physiological reasons of mechanical equipment and plants, the ventilation intensity of the general greenhouse is 0.75 air changes per minute to 1. 5 times, the temperature difference between inside and outside the greenhouse can be controlled within 5℃.
Tags:anti-reflective glass diffuse glass agricultural greenhouses glass greenhouse venlo greenhouse AR glass greenhouses glass agricultural glass horticultural glass #greenhouseglass #Antireflectiveglass #Diffusetemperedglass #Ultrawhitefloatglass #agriculturalgreenhouseglass #diffuseglass #horticulturalglass #Tomatogreenhouse #Coloredpeppergreenhouse #Lettucegreenhouse #Agriculturalgreenhouse #ARglass #venlogreenhouse #greenhouseglass #Antireflectiveglass #Diffusetemperedglass #Ultrawhitefloatglass #agriculturalgreenhouseglass #diffuseglass #horticulturalglass #Tomatogreenhouse #Coloredpeppergreenhouse #Lettucegreenhouse #Agriculturalgreenhouse #ARglass #venlogreenhouse #GlassManufacturer #invernadero #ArchitecturalGlass #ClearFloatGlass #FloatGlass
Previous:The technical process of soilless cultivation of tomatoes in smart glass greenhouses